Excavation Contractors St. Martin
Find the best Trenching Services in St. Martin
Receive 3 FREE Land Excavation quotes for your project today! Compare profiles, reviews, accreditations, portfolio, etc... and choose the best service.
- Gu
Gulf States Enterprises, Inc.
534 reviewsPensacola, US- Services
- Why Us?
- Gallery
Get Quote 
Jordon Construction, Inc.
Pensacola, 32526, USJordon Construction, Inc. With years of experience and an unwavering commitment to customer care and satisfaction, Jordon Construction, Inc. has become one of the most sought-after construction teams in the area. Our dedicated team has been trusted by business owners to plan, organize, and execute seamless construction and remodeling projects for years. For construction services that are unparalleled in every way, call to set up a consultation at (850) 554-8842. The Construction Company That Cares About Customer Satisfaction At Jordon Construction, Inc., we are not only working to meet the needs of our valued customers but to exceed them. From the initial meeting to the last coat of paint, our team is committed to going above and beyond for every client. Customer satisfaction means: Listening carefully to your vision Understanding your budget Helping you choose the best materials and services for your project Keeping you informed at every stage of the process Taking good care of your property Respecting the schedule Readily available to address your questions and concerns No matter the size or breadth of your proposed project, Jordon Construction, Inc. will treat it with the utmost care and dedication from the get-go. Qualified Experts and Reliable Materials We have access to the industry's most qualified subcontractors, modern machinery, and reliable materials. With the best resources, we drive to deliver beautiful, high-quality results that are built to withstand the test of time. Variety of Choices We offer a variety of choices in materials, finishes, floor plans, and newly available innovations. We can implement cutting edge technology, functional storage solutions, and modern designs into commercial spaces. Local Construction Company Our hardworking team, timely executions, accommodating professionals, and high-quality results have helped build our glowing reputation. If you are in the market for a remodel, renovation, or addition to your business space, Jordon Construction, Inc. is the team for you.
- Services
- Why Us?
- Gallery
Get Quote
Earth advocate LLC.
534 reviewsPensacola, USWelcome to Earth Advocate LLC We are a family owned and operated business that provides land clearing, excavating, and demolition services. I'm Camden Clayton, and I started this business in 2021 with the support of my wife, Mandy. Originally from Hokes Bluff, Alabama, we relocated to the Gulf Coast in 2018 to continue pursuing my love for fishing. When not out on the water, I also enjoy hunting out west. I have always had a passion for the great outdoors. My motto has always been it’s not work if you love what you do. Starting this business has always been a dream of mine. Our mission is simple yet profound: to deliver exceptional land altering services that lay the groundwork for your success. We believe in customer satisfaction, and we approach each project with integrity and professionalism. Why Choose Us? Choosing Earth Advocate LLC means choosing reliability, efficiency, and a team that understands the intricacies of your specific projects. Here's what sets us apart: Experience: With years of hands-on experience, we've tackled projects of all sizes and complexities. Precision: Our commitment to precision ensures that your project is executed flawlessly, meeting and exceeding your expectations. Customer-centric approach: We prioritize your needs and work collaboratively to achieve the desired results. Connect with Us Ready to embark on your excavation journey? Whether you're planning a residential, commercial, or industrial project, we're here to assist. Let's connect and discuss how we can bring your vision to life. Thank you for considering Earth Advocate LLC for your excavation and grading needs. We look forward to the opportunity of working with you.
- Services
- Why Us?
- Our Team
- Gallery
Get Quote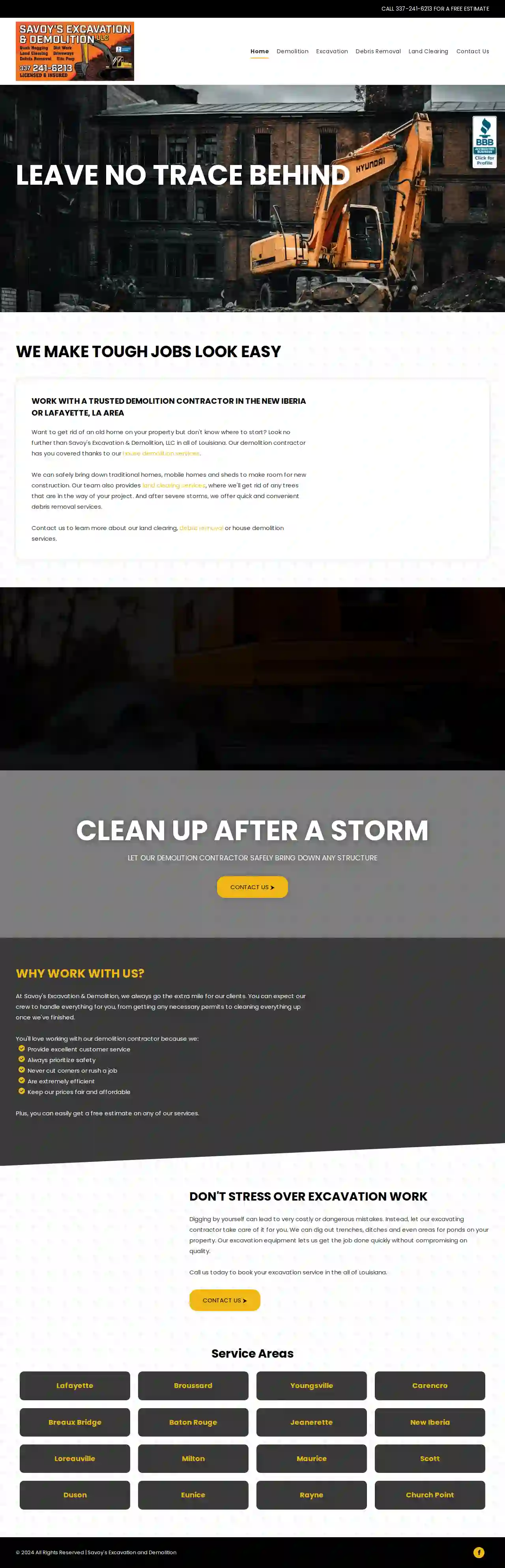
Savoy’s Excavation & Demolition llc
550 reviewsNew Iberia, LA 70560, 70560, USLet Our Demolition Contractor Safely Bring Down Any Structure Want to get rid of an old home on your property but don't know where to start? Look no further than Savoy's Excavation & Demolition, LLC in all of Louisiana. Our demolition contractor has you covered thanks to our house demolition services. We can safely bring down traditional homes, mobile homes and sheds to make room for new construction. Our team also provides land clearing services, where we'll get rid of any trees that are in the way of your project. And after severe storms, we offer quick and convenient debris removal services. Contact us to learn more about our land clearing, debris removal or house demolition services. Why Work With Us? At Savoy's Excavation & Demolition, we always go the extra mile for our clients. You can expect our crew to handle everything for you, from getting any necessary permits to cleaning everything up once we've finished. You'll love working with our demolition contractor because we: Provide excellent customer service Always prioritize safety Never cut corners or rush a job Are extremely efficient Keep our prices fair and affordable Plus, you can easily get a free estimate on any of our services. Don't Stress Over Excavation Work Digging by yourself can lead to very costly or dangerous mistakes. Instead, let our excavating contractor take care of it for you. We can dig out trenches, ditches and even areas for ponds on your property. Our excavation equipment lets us get the job done quickly without compromising on quality. Call us today to book your excavation service in the all of Louisiana.
- Services
- Why Us?
- Gallery
Get Quote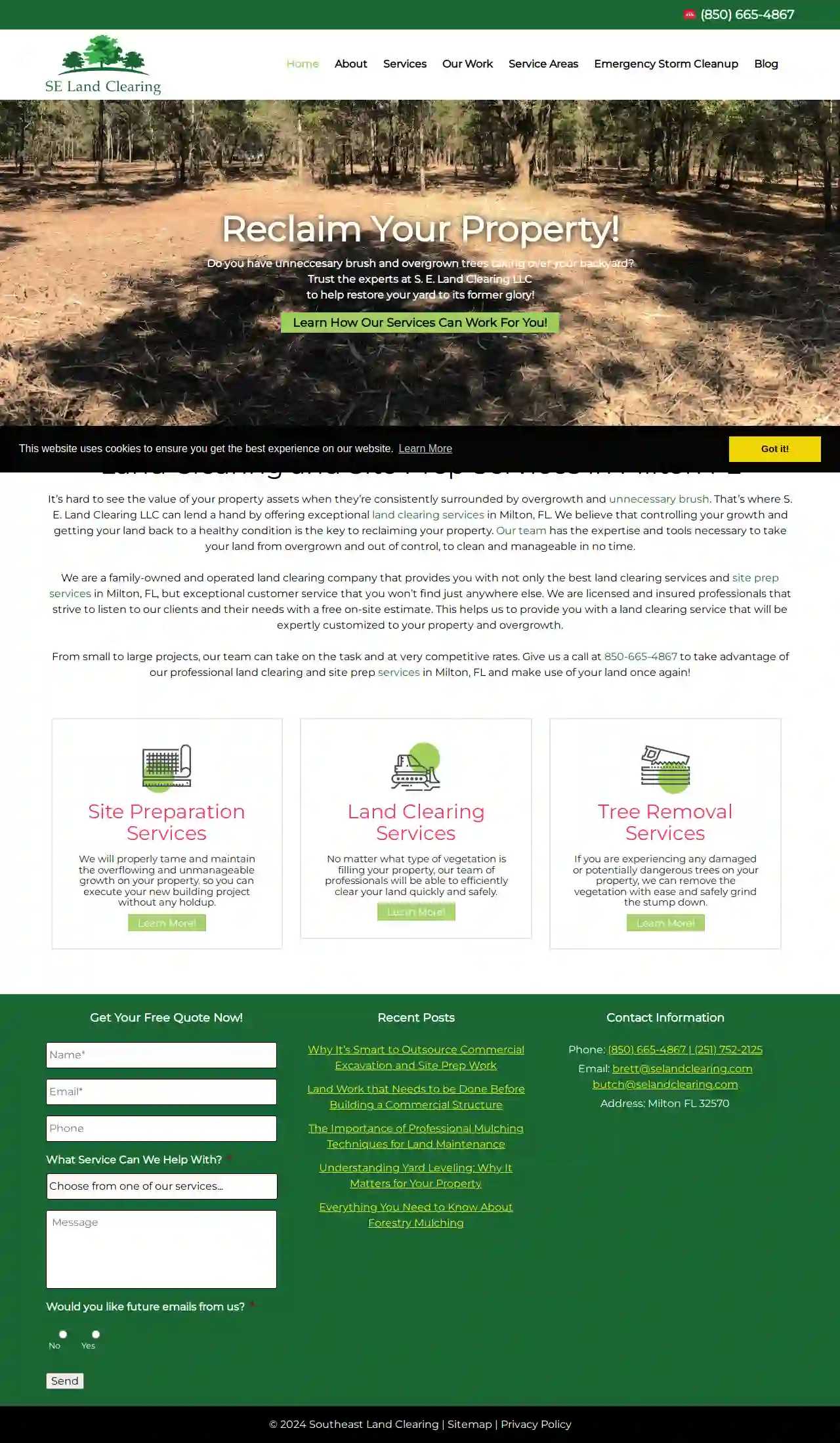
Southeast Land Clearing
4.511 reviewsMilton, 32570, USReclaim Your Property! Do you have unnecessary brush and overgrown trees taking over your backyard? Trust the experts at S. E. Land Clearing LLC to help restore your yard to its former glory! It’s hard to see the value of your property assets when they’re consistently surrounded by overgrowth and unnecessary brush. That’s where S. E. Land Clearing LLC can lend a hand by offering exceptional land clearing services in Milton, FL. We believe that controlling your growth and getting your land back to a healthy condition is the key to reclaiming your property. Our team has the expertise and tools necessary to take your land from overgrown and out of control, to clean and manageable in no time. We are a family-owned and operated land clearing company that provides you with not only the best land clearing services and site prep services in Milton, FL, but exceptional customer service that you won’t find just anywhere else. We are licensed and insured professionals that strive to listen to our clients and their needs with a free on-site estimate. This helps us to provide you with a land clearing service that will be expertly customized to your property and overgrowth. From small to large projects, our team can take on the task and at very competitive rates. Give us a call at 850-665-4867 to take advantage of our professional land clearing and site prep services in Milton, FL and make use of your land once again!
- Services
- Why Us?
- Testimonials
- Gallery
Get Quote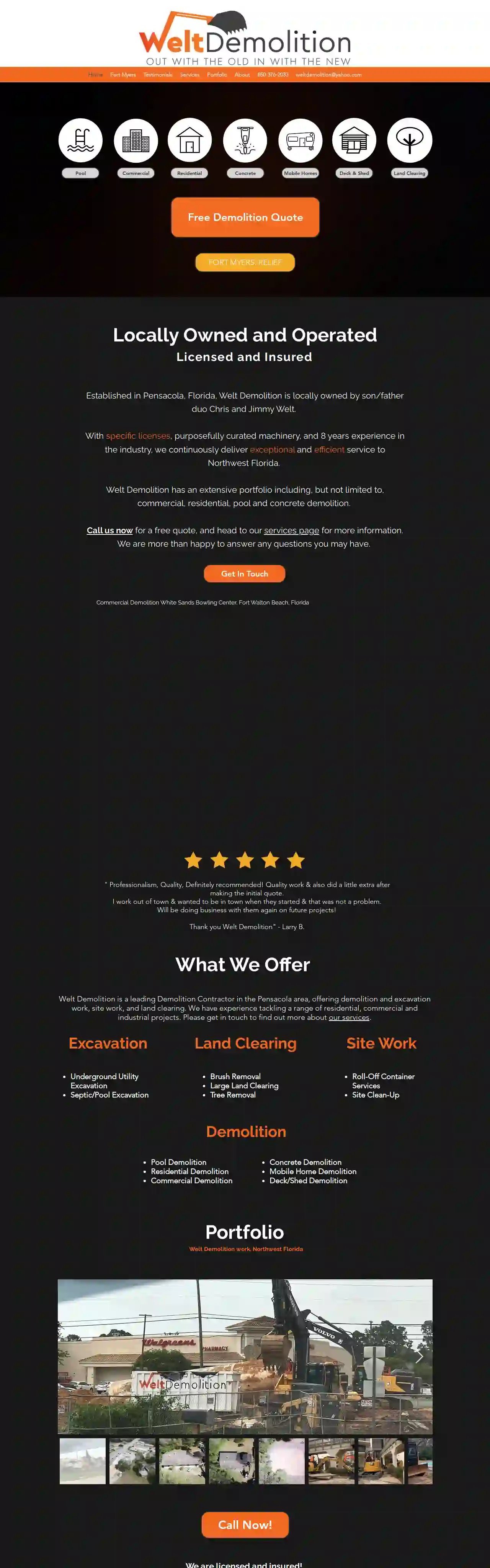
Welt Demolition
511 reviews1316 E Moreno St, Pensacola, 32503, USLocally Owned and Operated Established in Pensacola, Florida, Welt Demolition is locally owned by son/father duo Chris and Jimmy Welt. With specific licenses, purposefully curated machinery, and 8 years experience in the industry, we continuously deliver exceptional and efficient service to Northwest Florida. Welt Demolition has an extensive portfolio including, but not limited to, commercial, residential, pool and concrete demolition. Call us now for a free quote, and head to our services page for more information. We are more than happy to answer any questions you may have.
- Services
- Why Us?
- Testimonials
- Gallery
Get Quote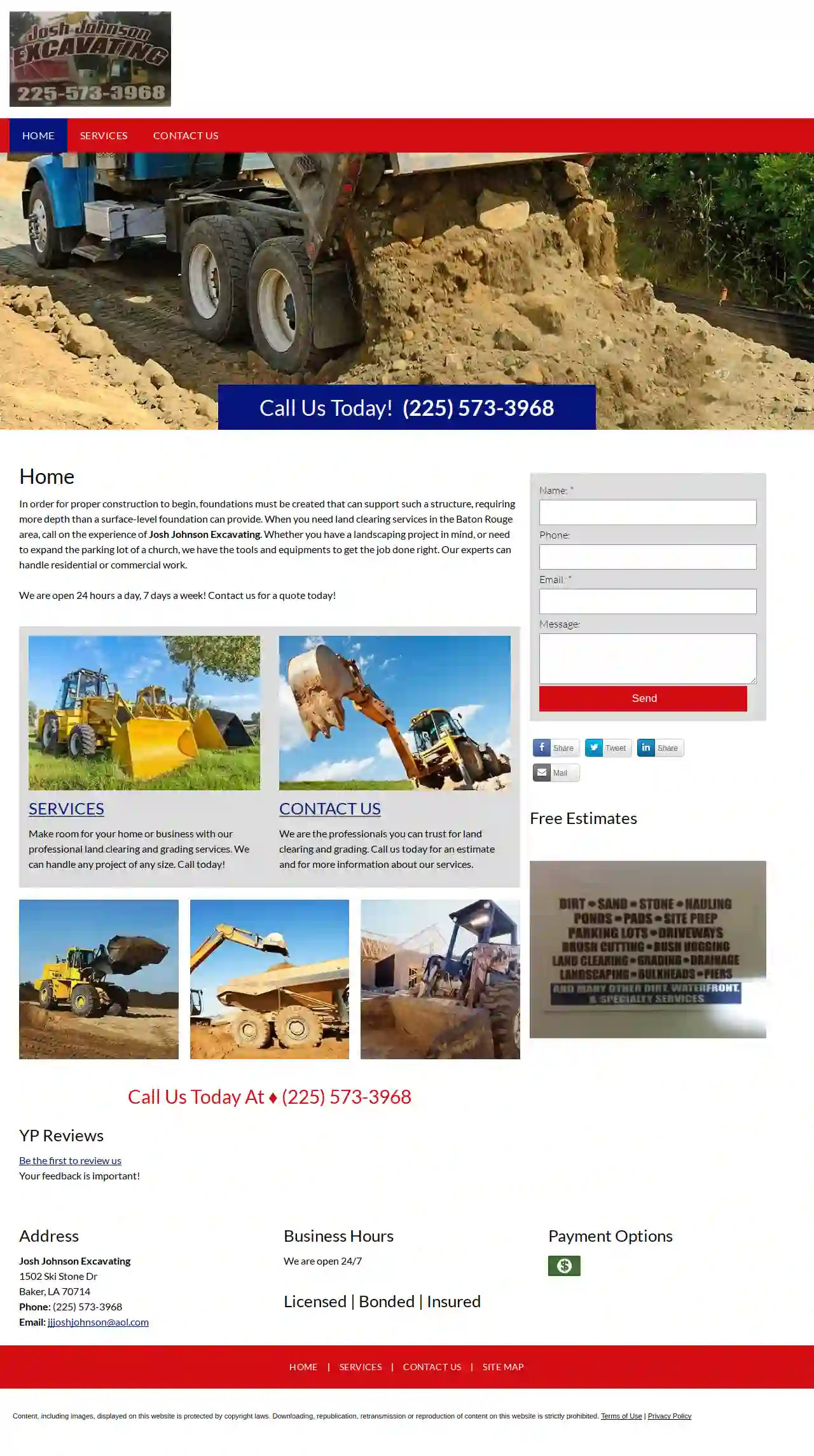
Josh Johnson Excavating
1502 Ski Stone Dr, Baker, 70714, USJosh Johnson Excavating: Your Trusted Partner for Land Clearing and Grading in Baton Rouge When it comes to preparing land for construction, whether it's a new home, a commercial development, or a landscaping project, a solid foundation is essential. That's where Josh Johnson Excavating comes in. We are a family-owned and operated business with over a decade of experience serving the Baton Rouge area. We understand the importance of meticulous site preparation and are committed to delivering high-quality results that meet your specific needs. Our team of skilled professionals is equipped with the latest tools and equipment to handle any project, big or small. We specialize in a wide range of services, including: • Land Clearing • Grading • Excavation • Dirt Work • Sand and Stone Hauling • Pond Construction • Site Preparation • Parking Lot Construction • Driveway Installation • Concrete Work • Brush Cutting • Bush Hogging • Drainage Solutions • Landscaping • Bulkheads • Piers We are dedicated to providing exceptional customer service and working closely with our clients to ensure their complete satisfaction. Our commitment to quality, efficiency, and safety is reflected in every project we undertake. Contact us today for a free estimate and let us help you bring your vision to life.
- Services
- Why Us?
- Gallery
Get Quote
JW2
514 reviews29715 Amvets Rd., Albany, 70711, USJW2 Co. - Your Land Development Experts JW2 Co. is your one-stop shop for all your land development needs. We specialize in forestry mulching, storm debris removal, food plots, shooting lanes, driveway maintenance, and more. We are committed to providing our clients with the highest quality services at competitive prices. Our team of experienced professionals is dedicated to exceeding your expectations. We offer financing options through Hearth, making it easier than ever to get the land development services you need. We are proud to serve the Albany, Louisiana area. Contact us today for a free quote!
- Services
- Why Us?
- Gallery
Get Quote
IDS Concrete Cutting (International Drilling & Sawing)
4.610 reviewsPensacola, USAbout Us IDS offers multiple services that can help aid in a demolition or remodel project. There is no job too big or too small for IDS to handle. We offer demolition, concrete cutting, GPR and radar imaging, removal and disposal, and dumpster rentals. Working Together IDS has been in business for over 29 years and offers an exceptional end-to-end client experience. We strive to be the company you can depend on time and time again. Why Choose Us? We're a woman-owned business in the construction industry and have helped thousands of customers complete their projects. We have the best team and tools in the business. Give us a chance and see what we're all about. CSDA Certification We are a CSDA Certified Operator. IDS Cuts is proud to be one of few distinct concrete cutting companies in the United States to be CSDA Certified. The Concrete Sawing & Drilling Association is a nonprofit trade association of contractors, manufacturers and affiliated members from the construction and renovation industry. Diamond tools for projects requiring sawing, drilling, selective demolition, cutting and polishing offers the construction industry many benefits including lower total project costs, precision cutting, maintenance of structural integrity, reduced downtime, reduced noise, dust and debris, limited access cutting and the ability to cut heavily-reinforced concrete. Founded in 1972, CSDA has 500 member companies worldwide.
- Services
- Why Us?
- Gallery
Get Quote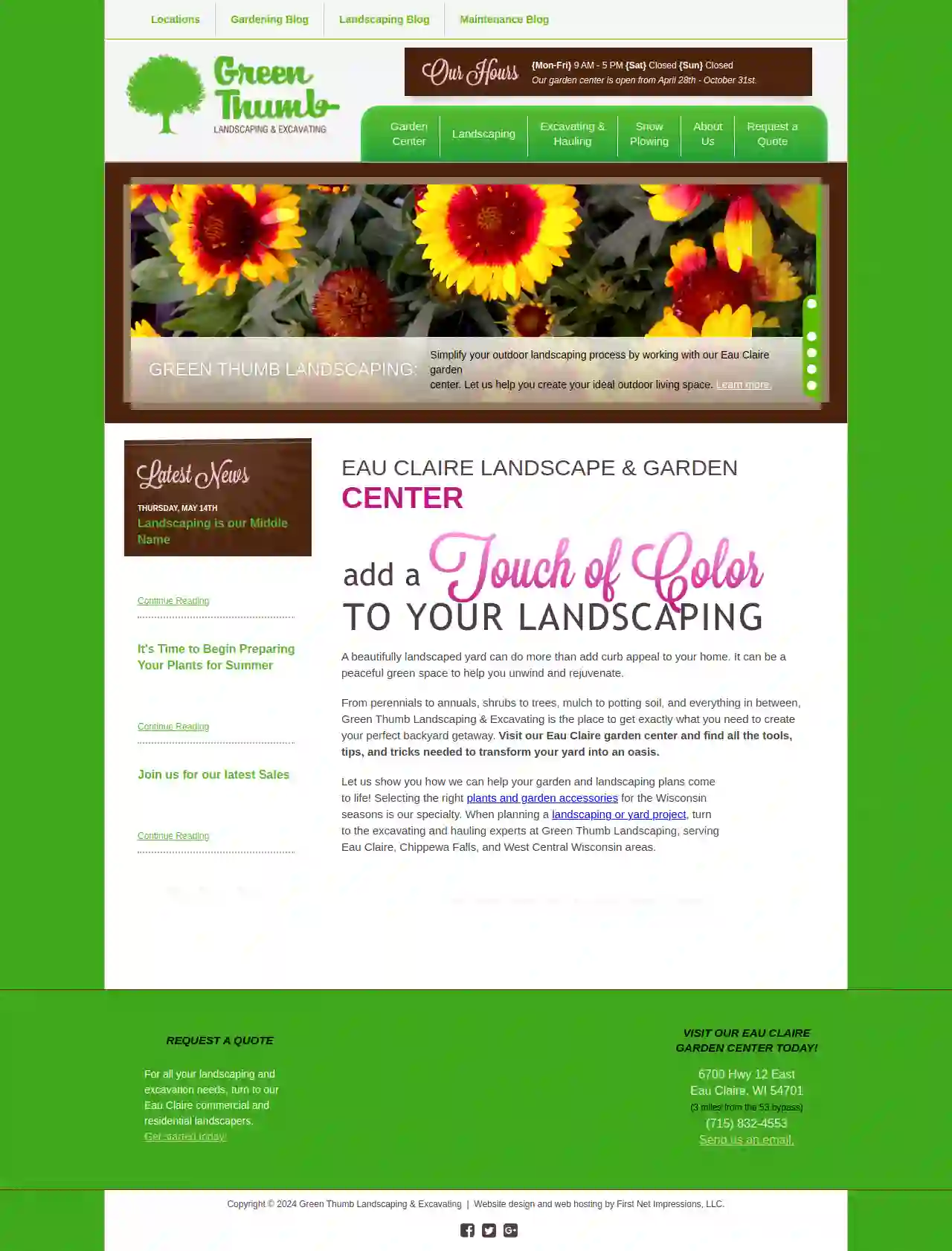
Green Thumb Landscaping & Excavating Inc
3.622 reviews6700 Hwy 12 East, Eau Claire, 54701, USEau Claire Landscape & Garden Center A beautifully landscaped yard can do more than add curb appeal to your home. It can be a peaceful green space to help you unwind and rejuvenate. From perennials to annuals, shrubs to trees, mulch to potting soil, and everything in between, Green Thumb Landscaping & Excavating is the place to get exactly what you need to create your perfect backyard getaway. Visit our Eau Claire garden center and find all the tools, tips, and tricks needed to transform your yard into an oasis. Let us show you how we can help your garden and landscaping plans come to life! Selecting the right plants and garden accessories for the Wisconsin seasons is our specialty. When planning a landscaping or yard project, turn to the excavating and hauling experts at Green Thumb Landscaping, serving Eau Claire, Chippewa Falls, and West Central Wisconsin areas. Learn More About Our Eau Claire Garden Center For all your landscaping and excavation needs, turn to our Eau Claire commercial and residential landscapers. Get started today!
- Services
- Why Us?
- Gallery
Get Quote
Over 22,076+ Excavation Businesses registered
Our excavation contractors operate in St. Martin & surrounding areas!
ExcavationHQ has curated and vetted Top Excavation Businesses arround St. Martin. Find a reliable business today.
Frequently Asked Questions About Excavation Contractors
- Planning and Surveying: Defining the excavation area, marking utility lines, and determining the required depth and grade.
- Site Preparation: Clearing vegetation, removing obstacles, and ensuring site accessibility.
- Excavation: Using appropriate equipment (excavators, backhoes, etc.) to remove earth and create the desired excavation.
- Hauling and Disposal: Transporting excavated material to designated disposal sites, complying with environmental regulations.
- Backfilling and Compaction: Refilling the excavation with suitable material and compacting it to achieve the required density and stability.
- Grading and Finishing: Leveling and shaping the surface to the final grade for landscaping or construction.
- Mechanical Excavation: Utilizing heavy equipment like excavators, backhoes, bulldozers, and loaders, suitable for most projects.
- Hand Excavation: Using hand tools (shovels, picks) for smaller excavations or delicate work near utilities.
- Blasting: Employing explosives to break up rock or hard materials, typically for large-scale projects.
- Hydro Excavation: Using high-pressure water jets to loosen and remove soil, often used for locating utilities or delicate excavation.
- Vacuum Excavation: Employing a vacuum system to suck up excavated material, suitable for safe excavation near utilities or in confined spaces.
- Spring and Fall: Often considered favorable due to moderate temperatures and drier soil conditions.
- Summer: Can be suitable, but hot weather can make working conditions challenging and might require additional measures (shade, hydration) for workers.
- Winter: Excavation in winter can be more difficult due to frozen ground, snow, and potential delays caused by inclement weather. It might also require specialized equipment or techniques.
- Soil Type and Stability: Stable, cohesive soils allow for deeper excavations than loose or unstable soils.
- Groundwater Level: Excavations below the water table require dewatering techniques to manage water intrusion.
- Equipment and Resources: The size and capabilities of excavation equipment influence the achievable depth.
- Safety Regulations: OSHA and other safety regulations impose limitations on trench depths without proper shoring or sloping.
- Project Requirements: The purpose of the excavation (basement, pool, foundation) determines the necessary depth.
What is the excavation process?
What are the different methods of excavation?
What is the best time of year for excavation?
How deep can you excavate?
What is the excavation process?
- Planning and Surveying: Defining the excavation area, marking utility lines, and determining the required depth and grade.
- Site Preparation: Clearing vegetation, removing obstacles, and ensuring site accessibility.
- Excavation: Using appropriate equipment (excavators, backhoes, etc.) to remove earth and create the desired excavation.
- Hauling and Disposal: Transporting excavated material to designated disposal sites, complying with environmental regulations.
- Backfilling and Compaction: Refilling the excavation with suitable material and compacting it to achieve the required density and stability.
- Grading and Finishing: Leveling and shaping the surface to the final grade for landscaping or construction.
What are the different methods of excavation?
- Mechanical Excavation: Utilizing heavy equipment like excavators, backhoes, bulldozers, and loaders, suitable for most projects.
- Hand Excavation: Using hand tools (shovels, picks) for smaller excavations or delicate work near utilities.
- Blasting: Employing explosives to break up rock or hard materials, typically for large-scale projects.
- Hydro Excavation: Using high-pressure water jets to loosen and remove soil, often used for locating utilities or delicate excavation.
- Vacuum Excavation: Employing a vacuum system to suck up excavated material, suitable for safe excavation near utilities or in confined spaces.
What is the best time of year for excavation?
- Spring and Fall: Often considered favorable due to moderate temperatures and drier soil conditions.
- Summer: Can be suitable, but hot weather can make working conditions challenging and might require additional measures (shade, hydration) for workers.
- Winter: Excavation in winter can be more difficult due to frozen ground, snow, and potential delays caused by inclement weather. It might also require specialized equipment or techniques.
How deep can you excavate?
- Soil Type and Stability: Stable, cohesive soils allow for deeper excavations than loose or unstable soils.
- Groundwater Level: Excavations below the water table require dewatering techniques to manage water intrusion.
- Equipment and Resources: The size and capabilities of excavation equipment influence the achievable depth.
- Safety Regulations: OSHA and other safety regulations impose limitations on trench depths without proper shoring or sloping.
- Project Requirements: The purpose of the excavation (basement, pool, foundation) determines the necessary depth.