Excavation Contractors San Jose
Find Land Excavation in San Jose
Receive up to 3 Excavating Contractors quotes for your project today! Compare profiles, reviews, accreditations, portfolio, etc... and choose the best offer.
Service Needed
City or Town
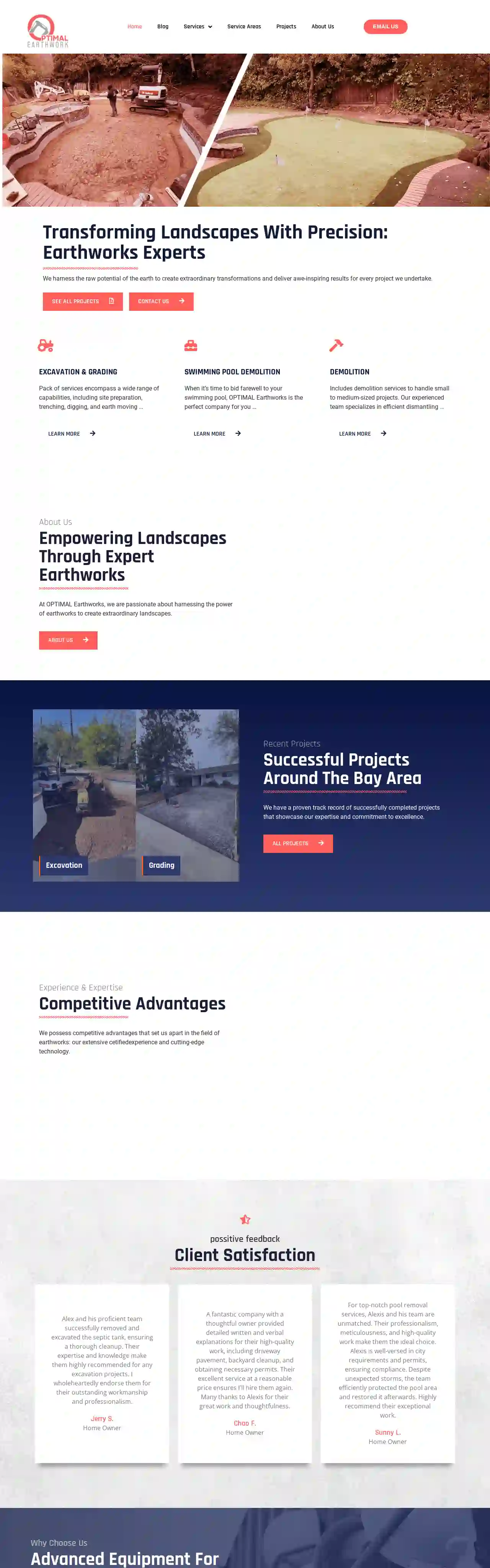
Optimal EarthWork
51 reviews3070 Garden Ave, San Jose, 95111, USTransforming Landscapes with Precision: Earthworks Experts We harness the raw potential of the earth to create extraordinary transformations and deliver awe-inspiring results for every project we undertake. Excavation & Grading Swimming Pool Demolition Demolition
- Services
- Why Us?
- Accreditations
- Our Team
- Testimonials
- Gallery
Get Quote
Over 3,943+ Excavation Pros on our platform
Our excavation providers operate in San Jose & surroundings!
ExcavationHQ has curated and vetted the Best Excavation Pros in and around San Jose. Find the most reliable pro today.
Frequently Asked Questions About Excavation Contractors
Find answers to common questions about excavation contractors and hiring excavation professionals in the USA.
- Determining Soil Suitability: Assessing whether the soil can support the intended structure or load.
- Recommending Foundation Types: Advising on the appropriate foundation design based on soil characteristics.
- Addressing Drainage and Erosion Issues: Providing solutions to manage water runoff and prevent erosion.
- Evaluating Slope Stability: Assessing the risk of landslides or soil movement on slopes.
- Building on challenging soil types (expansive clay, loose sand, etc.)
- Constructing large or complex structures
- Excavating near slopes or retaining walls
- Addressing drainage or erosion concerns
- Hauling to Designated Disposal Sites: Transporting excavated material to approved landfills or recycling centers.
- Recycling or Reuse: If suitable, some excavated soil might be recycled for other projects or reused on-site for landscaping or backfilling.
- Complying with Regulations: Adhering to local and environmental regulations for soil disposal to prevent contamination or illegal dumping.
- Experience: Choose contractors with a proven track record and years of experience in excavation projects similar to yours.
- Licensing and Insurance: Verify that they are properly licensed to operate in your area and carry adequate insurance to protect you from liability in case of accidents or damage.
- Equipment and Resources: Ensure they have the necessary equipment and resources to handle your project efficiently and safely.
- Positive Reviews and References: Check online reviews and testimonials from previous customers. Request references and contact them to inquire about their experience with the contractor.
- Professionalism: Opt for a company that communicates clearly, provides detailed and transparent estimates, and has a responsive and courteous team.
What is a soil engineer, and do I need one?
A soil engineer is a professional specializing in analyzing soil properties and their behavior under various conditions. They play a crucial role in:
What is the difference between excavation and grading?
While often used together, excavation and grading are distinct processes:
Excavation: Primarily involves removing earth or other materials from a site. It's about digging down and creating space.
Grading: Focuses on shaping and leveling the ground to a specific slope or elevation. It's about adjusting the existing terrain.
For example, you might excavate a foundation and then grade the surrounding area to ensure proper drainage and a level surface for landscaping.
Excavation: Primarily involves removing earth or other materials from a site. It's about digging down and creating space.
Grading: Focuses on shaping and leveling the ground to a specific slope or elevation. It's about adjusting the existing terrain.
For example, you might excavate a foundation and then grade the surrounding area to ensure proper drainage and a level surface for landscaping.
How do you handle soil disposal after excavation?
Responsible soil disposal after excavation is essential. Excavation contractors typically handle it by:
How do I find a good excavation contractor?
Finding a reputable excavation contractor involves careful research and consideration. Look for the following qualities:
What is a soil engineer, and do I need one?
A soil engineer is a professional specializing in analyzing soil properties and their behavior under various conditions. They play a crucial role in:
- Determining Soil Suitability: Assessing whether the soil can support the intended structure or load.
- Recommending Foundation Types: Advising on the appropriate foundation design based on soil characteristics.
- Addressing Drainage and Erosion Issues: Providing solutions to manage water runoff and prevent erosion.
- Evaluating Slope Stability: Assessing the risk of landslides or soil movement on slopes.
- Building on challenging soil types (expansive clay, loose sand, etc.)
- Constructing large or complex structures
- Excavating near slopes or retaining walls
- Addressing drainage or erosion concerns
What is the difference between excavation and grading?
While often used together, excavation and grading are distinct processes:
Excavation: Primarily involves removing earth or other materials from a site. It's about digging down and creating space.
Grading: Focuses on shaping and leveling the ground to a specific slope or elevation. It's about adjusting the existing terrain.
For example, you might excavate a foundation and then grade the surrounding area to ensure proper drainage and a level surface for landscaping.
Excavation: Primarily involves removing earth or other materials from a site. It's about digging down and creating space.
Grading: Focuses on shaping and leveling the ground to a specific slope or elevation. It's about adjusting the existing terrain.
For example, you might excavate a foundation and then grade the surrounding area to ensure proper drainage and a level surface for landscaping.
How do you handle soil disposal after excavation?
Responsible soil disposal after excavation is essential. Excavation contractors typically handle it by:
- Hauling to Designated Disposal Sites: Transporting excavated material to approved landfills or recycling centers.
- Recycling or Reuse: If suitable, some excavated soil might be recycled for other projects or reused on-site for landscaping or backfilling.
- Complying with Regulations: Adhering to local and environmental regulations for soil disposal to prevent contamination or illegal dumping.
How do I find a good excavation contractor?
Finding a reputable excavation contractor involves careful research and consideration. Look for the following qualities:
- Experience: Choose contractors with a proven track record and years of experience in excavation projects similar to yours.
- Licensing and Insurance: Verify that they are properly licensed to operate in your area and carry adequate insurance to protect you from liability in case of accidents or damage.
- Equipment and Resources: Ensure they have the necessary equipment and resources to handle your project efficiently and safely.
- Positive Reviews and References: Check online reviews and testimonials from previous customers. Request references and contact them to inquire about their experience with the contractor.
- Professionalism: Opt for a company that communicates clearly, provides detailed and transparent estimates, and has a responsive and courteous team.