Excavation Contractors League City
Best Excavating Contractors in League City
Receive multiple Excavation Company Near Me quotes for your project today! Compare profiles, reviews, accreditations, portfolio, etc... and choose the best deal.
Sundt Construction
49 reviewsSan Antonio, USAbout Sundt Sundt is committed to being the most skilled builder in America, owned and led by the industry’s top construction professionals. Our diverse expertise serves clients across the United States. History Founded in 1890, Sundt has a storied history of landmark projects across the country. Our Team As a 100% employee-owned company, we are committed to collaboration and accountability: shared responsibility and shared success. Sundt Foundation The Sundt Foundation reflects our employee-owners’ passion for giving back to the communities where we live and work. Our Regions As one of America’s largest and most respected general contractors, we have a portfolio of projects and roots spanning coast to coast. Awards & Recognition Our accomplishments reflect our employee-owners’ efforts and the spirit of cooperation and partnership we share with our clients.
- Services
- Why Us?
- Gallery
Get Quote
J. Dreyer's Excavating and Road Construction
53 reviewsPurcellville, USAbout J Dreyer's Excavators With over 30 years of experience, Jed Dreyer has helped hundreds of customers with their excavating and land moving needs. We strive to meet your needs and ensure that every job is done right the first time. With a commitment to quality and service we know how to find the right balance that meets your budget. If you are ready to take on a large excavating project or even a small road construction or pond building project, we can help.J. Dreyer's Excavators offers top of the line equipment and an artistic eye. Contact us today to see how we can assist you in creating the project of your dreams.
- Services
- Why Us?
- Our Team
- Testimonials
- Gallery
Get Quote
R. Integrity Design LLC
55 reviewsCleveland, Texas, USIntroducing R. Integrity Design LLC Are you looking for an experienced excavation contractor in Cleveland, TX? At R. Integrity Design LLC, our excavation services are rooted in a steadfast commitment to customer satisfaction. For over two decades, we have ensured that every project we undertake meets the highest standards of quality and safety. We understand the critical role that site preparation plays in any construction project, whether it's for a cozy home or a sprawling commercial complex. Our quick service doesn’t compromise on quality, and our reputation for great customer service is a testament to our client commitments. Our range of services is as diverse as our client base. From precise site clearing that paves the way for new beginnings to demolition services that carefully dismantle the old, we handle each task with unparalleled expertise. Our team excels in land demolition, clearing sites with efficiency and safety. We provide essential grading services like regrading and resloping to lay the ideal foundation for your construction. In construction demolition, we’re meticulous, ensuring precision in every phase. Our subgrade stabilization strengthens the base of your projects, and we’re adept at constructing retention walls, crucial for soil erosion and water flow control in civil constructions. Our work in specialized projects like railroad sighting, railroad yards, and railroad crossings showcases our versatility and ability to tackle complex tasks. We provide materials like gravel, crushed concrete, and limestone, integral to various construction phases. What sets R. Integrity Design LLC apart is our unwavering dedication to delivering exceptional service at great prices. We offer free estimates, ensuring transparency right from the start. For top-notch excavation services in Cleveland, TX, choose R. Integrity Design LLC. We're ready to bring your construction visions to life with our expertise. Reach out for a free estimate and discover why we're a go-to contractor in the industry. Together, let's create something outstanding.
- Services
- Why Us?
- Gallery
Get Quote
Austin Construction LLC
4.65 reviews5054 County Route 125, Campbell, 14821, USElliott Construction Services, LLC Elliott Construction Services, LLC is a HUBZONE certified company offering a wide range of services for residential, commercial, and institutional projects. We are located just minutes off of exit 41 on Interstate 86 in Campbell, NY, making us conveniently located for projects in the Southern Tier region of New York. Our team has extensive experience in all types of excavation, site development & grading, land clearing, demolition, pond building, septic system investigation & installation, drainage, water line installation, stone driveway repair & installation, asphalt repair, driveways & parking lots, concrete sidewalks, pads & foundations, concrete retaining walls, concrete & stone pavers, topsoil & seeding, trucking, gravel, and stone deliveries. We are committed to providing high-quality workmanship and exceptional customer service. Our team is dedicated to providing our clients with the highest quality services and exceeding their expectations. We are committed to safety, efficiency, and environmental responsibility in all our projects. We are proud to be HUBZONE certified, which allows us to provide competitive pricing and exceptional service to our clients.
- Services
- Why Us?
- Gallery
Get Quote
EarthX
4.312 reviews2439 E. St. Vrain Street, Colorado Springs, 80909, USAbout Us & Why We are The Best For the Job EarthX is Colorado’s premier landscaping choice, specializing in landscape construction of commercial projects, parks, and sport fields, as well as services surrounding property maintenance, land reclamation and erosion control. Our Story Enriching the lives of our customers and employees, while also preserving our nation’s waterways, forests, and natural resources to help sustain a positive future for generations to come. Our Leaders Since contracting with EarthX in 2019 for several communities, my landscaping issues have diminished greatly. EarthX is one of very few landscape contractors that is willing to quickly address individual homeowner issues. The attention to detail and multiple options presented for each problem allows me to fit all types of repairs and improvements into tight budgets. Last, but certainly not least, EarthX does not nickel and dime for irrigation repairs and takes ownership for their own mistakes or issues along the way. I would recommend EarthX to any fellow community managers for ongoing landscape maintenance and for large landscape installation projects for newer communities. Alex Carlson VP of Operations Centennial Consulting Group As a real estate developer, we oversee many commercial and residential properties throughout the Colorado front range. We have used EarthX for many years for everything from building fences and installing parks to installing and maintaining landscapes. Their excellent work has been instrumental in improving the appearance and function of every property. They are easy to work with, consistent, and good at what they do. Their costs are very fair. You always know when you hire EarthX that the job will be done in a timely manner and be done right. They are also very responsive and address any issue that comes up in a timely manner. Thanks, EarthX! Chasity McMorrow Colorado Springs I’ve been using EarthX for several years now. I always feel like a priority, regardless of the scale of the work I am requesting. They are easy to get a hold of and have been very responsive. The quality of work is top-notch and is always reasonably priced. The team at EarthX came out to my house and gave me a free estimate and consultation for a recent project. The work was scheduled and completed just a week later. The new grass looks great, and my irrigation system runs more efficiently than ever. I’ve recommended EarthX to all my family and friends. Ben PetersonColorado Springs
- Services
- Why Us?
- Testimonials
- Gallery
Get Quote- EC
ECO Restoration
1Spring, US- Services
- Why Us?
- Gallery
Get Quote 
Pira Consultants, Inc.
1409 Higgins St., Humble, 77338, USAbout Pira Consultants, Inc. Pira Consultants, Inc., established in 1982, is a seasoned excavating contractor serving Houston and its surrounding areas. We bring over 30 years of experience and unmatched expertise to every project we undertake, regardless of size. Our commitment to quality and customer satisfaction has made us a trusted name in the industry. We are dedicated to providing our clients with the highest level of service and professionalism.
- Services
- Why Us?
- Gallery
Get Quote
CES Excavation
1123 Main Street, City, 12345, USCES Excavation: Your Trusted Partner for Excavation Services CES Excavation is a reputable and experienced excavation company serving the [CITY] area. We are committed to providing high-quality excavation services for residential, commercial, and industrial projects. Our team of skilled and experienced operators utilizes state-of-the-art equipment to ensure efficient and safe completion of every project. We take pride in our attention to detail and commitment to customer satisfaction. Whether you need site preparation, foundation excavation, utility installation, or any other excavation service, CES Excavation is your reliable partner. We work closely with our clients to understand their specific needs and deliver exceptional results. Contact us today for a free consultation and let us help you bring your project to life.
- Services
- Why Us?
Get Quote
BBX Excavation
51 reviews123 Main Street, City, 12345, USAbout BBX Dirt BBX Dirt is a family-owned and operated business with over 20 years of experience in the dirt and topsoil industry. We are committed to providing our customers with the highest quality products and services at competitive prices. We offer a wide variety of dirt and topsoil products to meet the needs of both residential and commercial customers. Our team of experienced professionals is dedicated to providing our customers with the best possible service. We are proud to be a trusted source for dirt and topsoil in the [City, State] area. We are committed to providing our customers with the highest quality products and services at competitive prices. We offer a wide variety of dirt and topsoil products to meet the needs of both residential and commercial customers. Our team of experienced professionals is dedicated to providing our customers with the best possible service. We are proud to be a trusted source for dirt and topsoil in the [City, State] area. We are committed to providing our customers with the highest quality products and services at competitive prices. We offer a wide variety of dirt and topsoil products to meet the needs of both residential and commercial customers. Our team of experienced professionals is dedicated to providing our customers with the best possible service. We are proud to be a trusted source for dirt and topsoil in the [City, State] area.
- Services
- Why Us?
Get Quote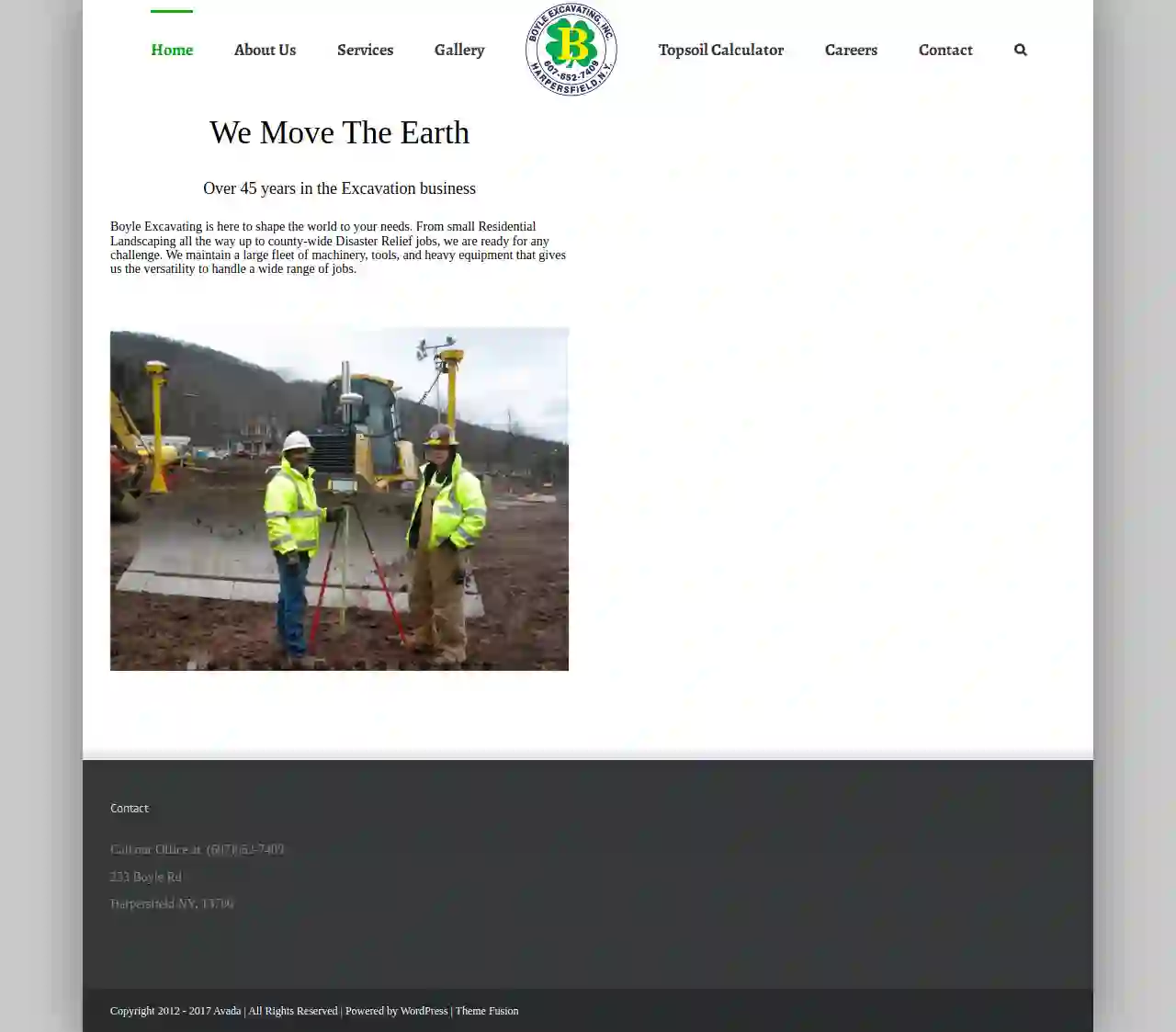
Boyle Excavating Inc
4.912 reviews233 Boyle Road, Harpersfield, 13786, USBoyle Excavating: Over 45 Years of Experience Boyle Excavating has been shaping the world to meet your needs for over 45 years. From small residential landscaping projects to large-scale county-wide disaster relief efforts, we're ready to tackle any challenge. Our extensive fleet of machinery, tools, and heavy equipment provides the versatility to handle a wide range of jobs. Our commitment to using the latest technology ensures our customers receive the best possible results. We believe in staying ahead of the curve, as technology is constantly evolving. We're passionate about our work and excited to see what each new day brings. We take pride in transforming dreams into reality, working closely with construction managers who recognize our dedication and ability to handle any task. Our team of dedicated and loyal employees is the backbone of our success, allowing us to deliver exceptional quality in every project.
- Services
- Why Us?
- Our Team
- Gallery
Get Quote
Over 3,943+ Excavation Contractors in our network
Our excavation pros operate in League City and surrounding areas!
ExcavationHQ has curated and vetted the Best Excavation Pros arround League City. Find a top & reliable pro today.
Frequently Asked Questions About Excavation Contractors
- Experience: Choose contractors with a proven track record and years of experience in excavation projects similar to yours.
- Licensing and Insurance: Verify that they are properly licensed to operate in your area and carry adequate insurance to protect you from liability in case of accidents or damage.
- Equipment and Resources: Ensure they have the necessary equipment and resources to handle your project efficiently and safely.
- Positive Reviews and References: Check online reviews and testimonials from previous customers. Request references and contact them to inquire about their experience with the contractor.
- Professionalism: Opt for a company that communicates clearly, provides detailed and transparent estimates, and has a responsive and courteous team.
- Spring and Fall: Often considered favorable due to moderate temperatures and drier soil conditions.
- Summer: Can be suitable, but hot weather can make working conditions challenging and might require additional measures (shade, hydration) for workers.
- Winter: Excavation in winter can be more difficult due to frozen ground, snow, and potential delays caused by inclement weather. It might also require specialized equipment or techniques.
- Project Size and Scope: Larger, more complex excavations naturally take longer.
- Soil Conditions: Rocky or challenging soil types can slow down progress.
- Site Accessibility: Limited access might require more time for maneuvering equipment and hauling materials.
- Weather: Inclement weather can cause delays.
- Permitting and Inspections: Waiting for permits or inspections can extend the timeline.
- Determining Soil Suitability: Assessing whether the soil can support the intended structure or load.
- Recommending Foundation Types: Advising on the appropriate foundation design based on soil characteristics.
- Addressing Drainage and Erosion Issues: Providing solutions to manage water runoff and prevent erosion.
- Evaluating Slope Stability: Assessing the risk of landslides or soil movement on slopes.
- Building on challenging soil types (expansive clay, loose sand, etc.)
- Constructing large or complex structures
- Excavating near slopes or retaining walls
- Addressing drainage or erosion concerns
How do I find a good excavation contractor?
What is the best time of year for excavation?
How long does an excavation project take?
What is a soil engineer, and do I need one?
How do I find a good excavation contractor?
- Experience: Choose contractors with a proven track record and years of experience in excavation projects similar to yours.
- Licensing and Insurance: Verify that they are properly licensed to operate in your area and carry adequate insurance to protect you from liability in case of accidents or damage.
- Equipment and Resources: Ensure they have the necessary equipment and resources to handle your project efficiently and safely.
- Positive Reviews and References: Check online reviews and testimonials from previous customers. Request references and contact them to inquire about their experience with the contractor.
- Professionalism: Opt for a company that communicates clearly, provides detailed and transparent estimates, and has a responsive and courteous team.
What is the best time of year for excavation?
- Spring and Fall: Often considered favorable due to moderate temperatures and drier soil conditions.
- Summer: Can be suitable, but hot weather can make working conditions challenging and might require additional measures (shade, hydration) for workers.
- Winter: Excavation in winter can be more difficult due to frozen ground, snow, and potential delays caused by inclement weather. It might also require specialized equipment or techniques.
How long does an excavation project take?
- Project Size and Scope: Larger, more complex excavations naturally take longer.
- Soil Conditions: Rocky or challenging soil types can slow down progress.
- Site Accessibility: Limited access might require more time for maneuvering equipment and hauling materials.
- Weather: Inclement weather can cause delays.
- Permitting and Inspections: Waiting for permits or inspections can extend the timeline.
What is a soil engineer, and do I need one?
- Determining Soil Suitability: Assessing whether the soil can support the intended structure or load.
- Recommending Foundation Types: Advising on the appropriate foundation design based on soil characteristics.
- Addressing Drainage and Erosion Issues: Providing solutions to manage water runoff and prevent erosion.
- Evaluating Slope Stability: Assessing the risk of landslides or soil movement on slopes.
- Building on challenging soil types (expansive clay, loose sand, etc.)
- Constructing large or complex structures
- Excavating near slopes or retaining walls
- Addressing drainage or erosion concerns